0ocyte aspiration needle double lumen
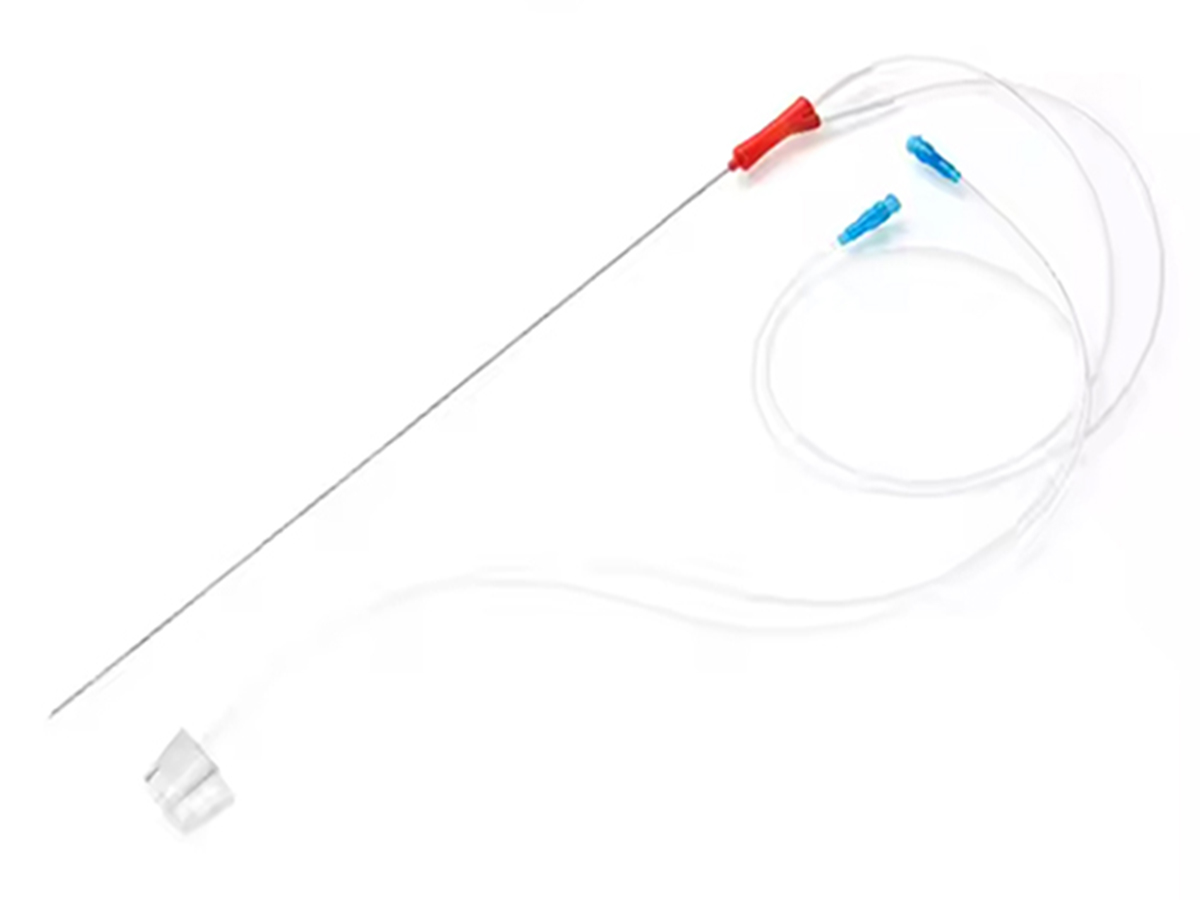
A double lumen oocyte aspiration needle is a specialized medical device used in oocyte retrieval during in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures. Its primary function is to extract oocytes (eggs) from the ovarian follicles after ovarian stimulation. The "double lumen" design offers several advantages over the more common single-lumen needles, particularly in terms of efficiency and reducing trauma to the ovaries.
Key Features of a Double Lumen Oocyte Aspiration Needle:
Double Lumen Design:
- Two Separate Channels (Lumens):
- One lumen is used for aspiration—to suction and collect the follicular fluid along with the oocyte.
- The second lumen is for flushing the follicle with a saline solution to help dislodge the oocyte and improve the chances of retrieving the egg.
- Two Separate Channels (Lumens):
Advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: The flushing mechanism of the second lumen can help retrieve oocytes from follicles that might not release eggs easily. This can result in higher oocyte yield compared to single-lumen needles.
- Reduced Need for Multiple Punctures: Since the needle both aspirates and flushes, it reduces the number of times the needle needs to be inserted into the ovary, minimizing trauma.
- Minimized Ovarian Damage: Fewer insertions can help reduce the risk of bleeding, ovarian damage, and discomfort for the patient.
Procedure:
- During oocyte retrieval, the needle is guided through the vaginal wall and into the ovary, typically under ultrasound guidance.
- The first lumen aspirates the follicular fluid containing the oocyte, while the second lumen can flush the follicle if the oocyte is not readily aspirated.
- Once the fluid is collected, it is immediately inspected under a microscope to identify and isolate the oocyte.
Applications:
- IVF Procedures: Primarily used in IVF to retrieve oocytes after ovarian stimulation.
- Difficult-to-Retrieve Oocytes: Particularly useful when oocytes are difficult to aspirate, as flushing the follicle can help dislodge them.
The double lumen needle helps in increasing the success rate of oocyte retrieval by improving the efficiency of the procedure while minimizing trauma to the patient.