Silicone gastrostomy tube
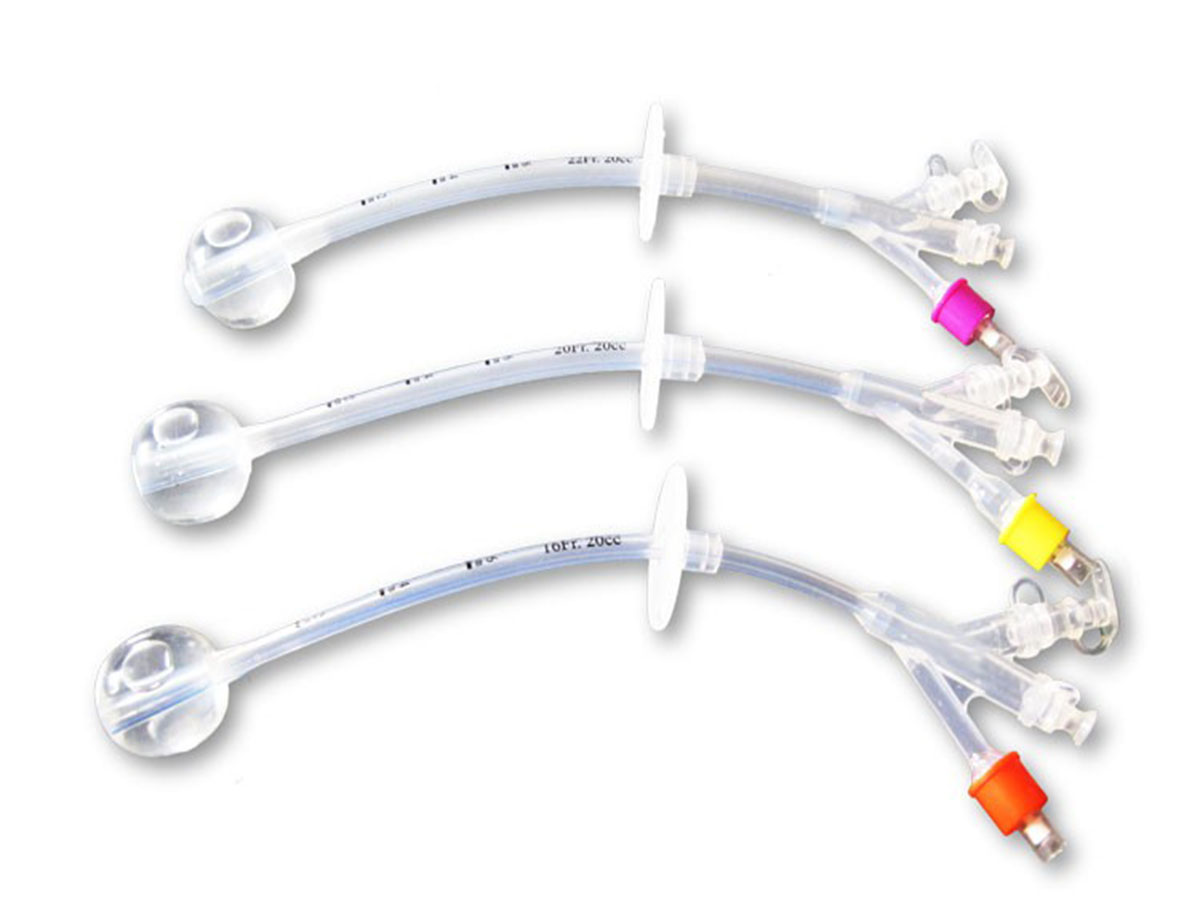
A silicone gastrostomy tube is a medical device inserted through the abdomen directly into the stomach to provide nutrition, fluids, and medications when oral intake is not possible or adequate. Gastrostomy tubes (commonly referred to as G-tubes) are often made from medical-grade silicone due to its flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to degradation within the body.
Key Features:
- Material: Silicone is soft, flexible, and durable, making it comfortable for patients. It is less likely to cause irritation or allergic reactions compared to other materials.
- Design: The tube typically has a balloon or bumper inside the stomach to keep it securely in place.
- Multiple Openings: These tubes often have side ports for easier drainage, feeding, or medication delivery.
Common Uses:
- Long-term feeding: For patients who cannot swallow due to conditions like stroke, neurological disorders, or head and neck cancers.
- Post-surgery nutrition: Used after surgeries that temporarily impair swallowing or digestion.
- Chronic illnesses: For conditions that interfere with normal food intake, such as esophageal cancer or severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Types of Silicone Gastrostomy Tubes:
- Balloon G-tube: Held in place by an inflatable balloon inside the stomach. It can be easily replaced without surgery.
- Non-balloon G-tube: Has an internal bumper that keeps the tube in place, offering a more secure but less flexible option.
- Low-profile "button" tubes: These sit flush with the skin, reducing the risk of accidental dislodgement and are less noticeable under clothing.
Advantages of Silicone:
- Biocompatibility: Minimizes irritation or allergic reactions.
- Flexibility and comfort: More comfortable for long-term use compared to harder materials.
- Durability: Resistant to breakdown from stomach acid and bodily fluids.
Maintenance:
- Cleaning: Requires daily cleaning around the stoma site to prevent infection.
- Replacement: Depending on the type, silicone G-tubes may need periodic replacement, especially balloon-based ones, as the balloon can degrade over time.
Would you like more details on insertion techniques, tube care, or specific types of gastrostomy tubes?